Italy - Renaissance (1400 - 1700)
-
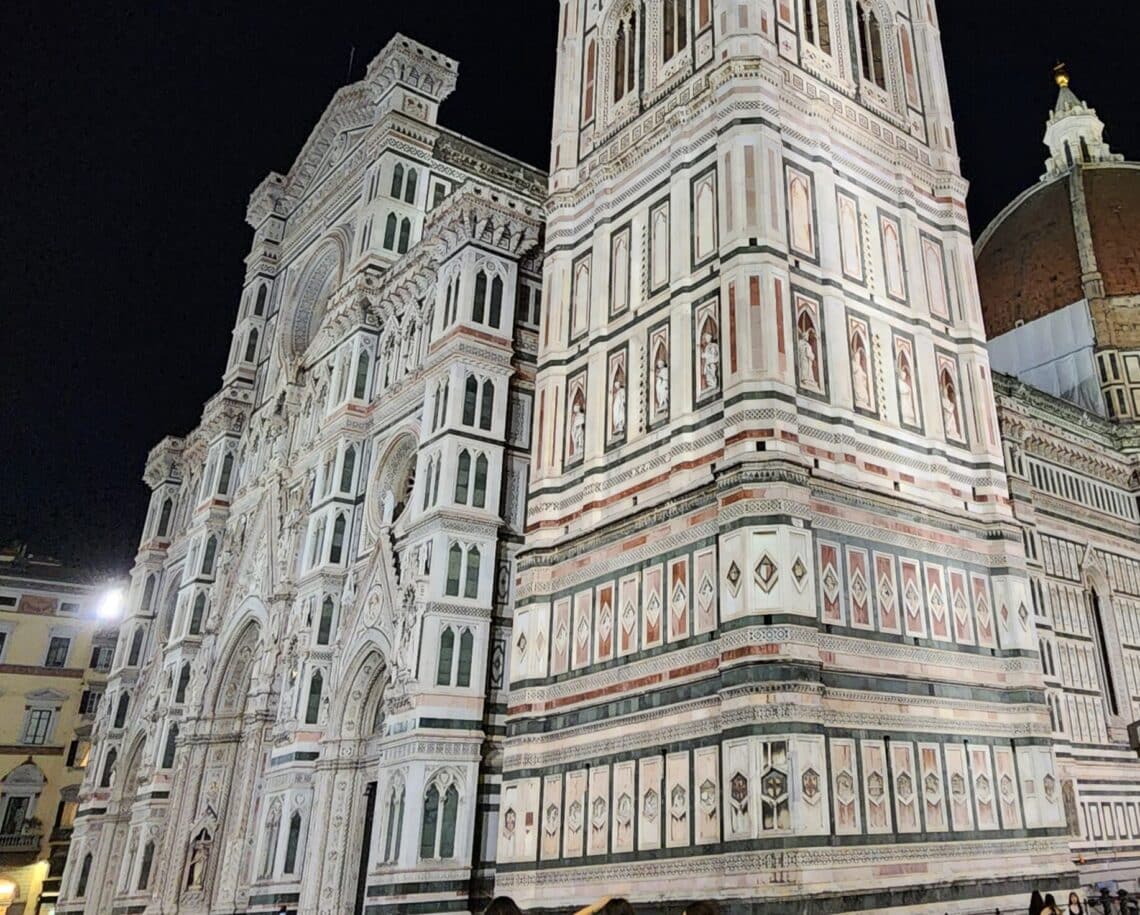
The sparkling Duomo in the darkness
The sparkling Duomo in the darkness Il duomo scintillante nel buio Stone outlined in green and rose and white As if it were paper cut out by giant’s hand As if the stone itself glows with inner light Tourists, unthinking, circumambulating this glimmering Kaaba. Like them, I am in awe, shivering at its wonder Tier upon tier, panel upon panel drawing eye upward Into lost and questioning darkness above This endless flow of humanity, come to worship its beauty Do we do well to come here? And in the beauty, do we find some echo of the nameless? Pietra tracciata di verde, rosa e bianco Come se fosse carta tagliata…
-
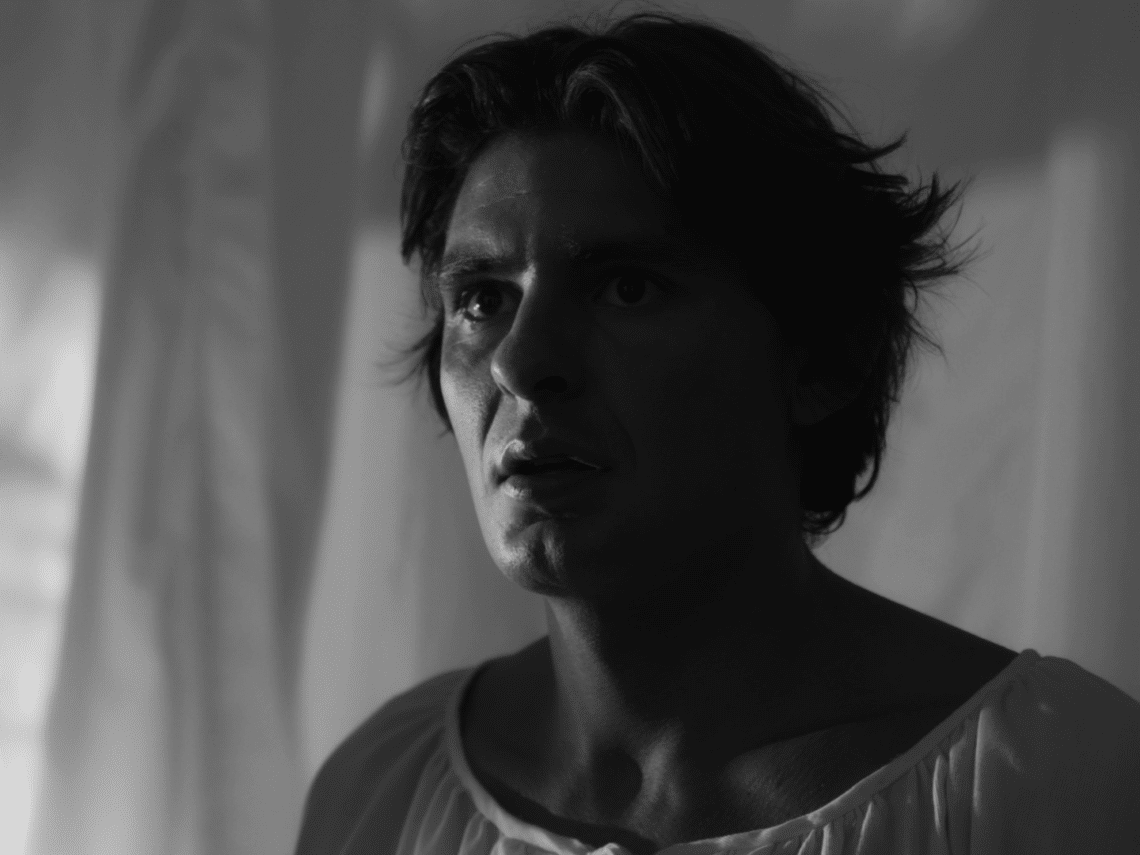
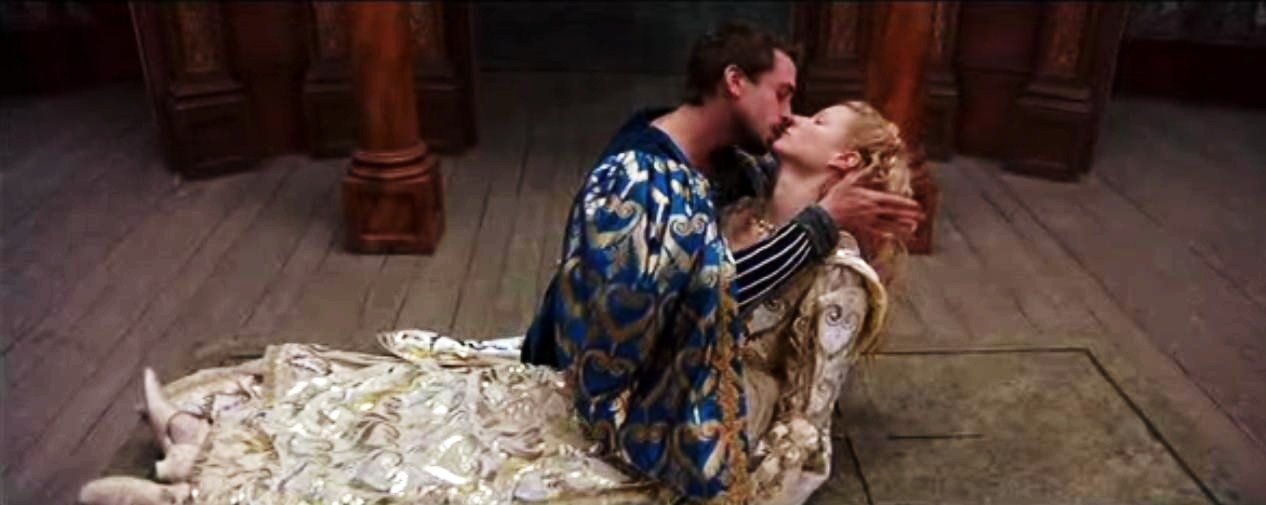
Juliet is dead! In world first, Australian team films lost historical Romeo scene.
Press Release: Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet has long entranced audiences worldwide, but what if there’s more to the story? In a groundbreaking first, an Australian team unveils a powerful scene from Matteo Bandello’s overlooked original Italian version, Romeo and Giulietta, which Shakespeare adapted. “Even though Romeo and Juliet is set in Verona, most people don’t know it’s an Italian story,” explains Italian-Australian author Michael Curtotti, who recently unveiled a fresh English translation of Matteo Bandello’s narrative. “It’s like appreciating Peter Jackson’s Lord of the Rings without acknowledging JRR Tolkien. Within Bandello’s rendition lies a trove of narrative richness that was left on the cutting room floor.” Led by director Rhianna…
-
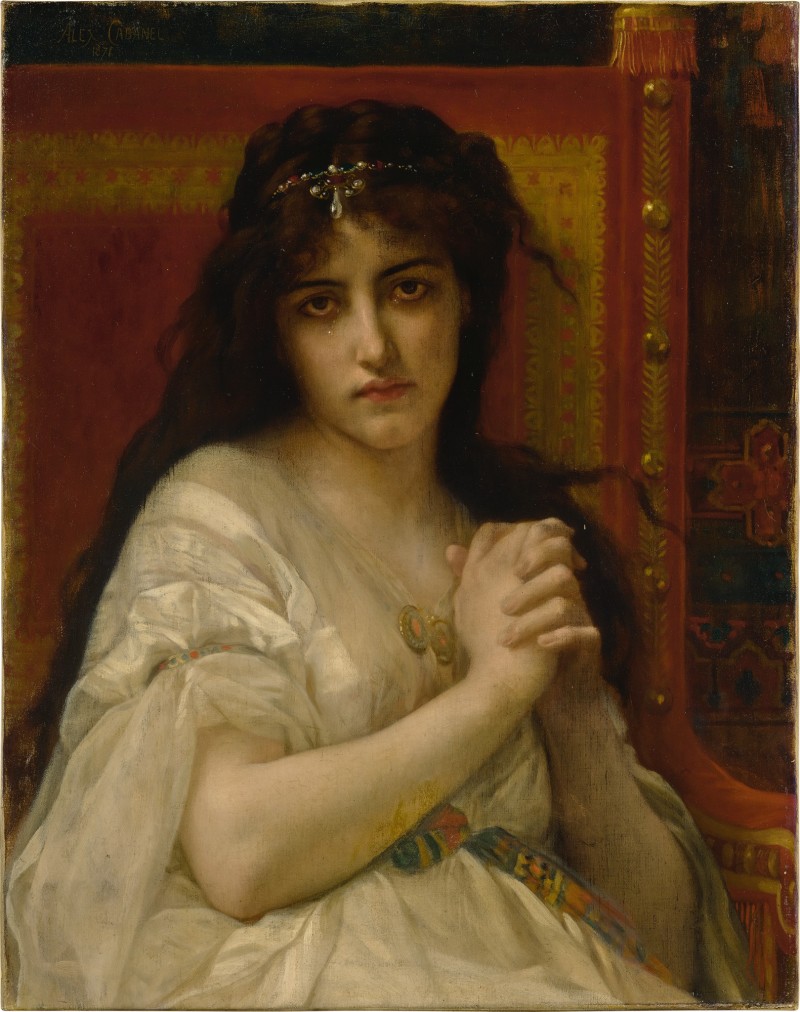
Othello and Desdemona: An Italian novella of murder and manipulation
Until you read the stories that Shakespeare read, it’s difficult to fully understand the plays he wrote. This is the tale of a particular story he read: the Italian novella which inspired Othello. Shakespeare adapted its plot to the stage, and like Romeo and Juliet, he made it world famous. To Shakespeare, Othello was the most important person in the tale. For the author of the novella however, Desdemona was the heart of the story. For the novella focusses on hatred of a woman. In Shakespeare’s hands the story became a play about the hatred of a man. There is much that the two stories share in common. Most of…
-
An Interview with Dr Francesco Ricatti: Matteo Bandello’s Romeo and Juliet
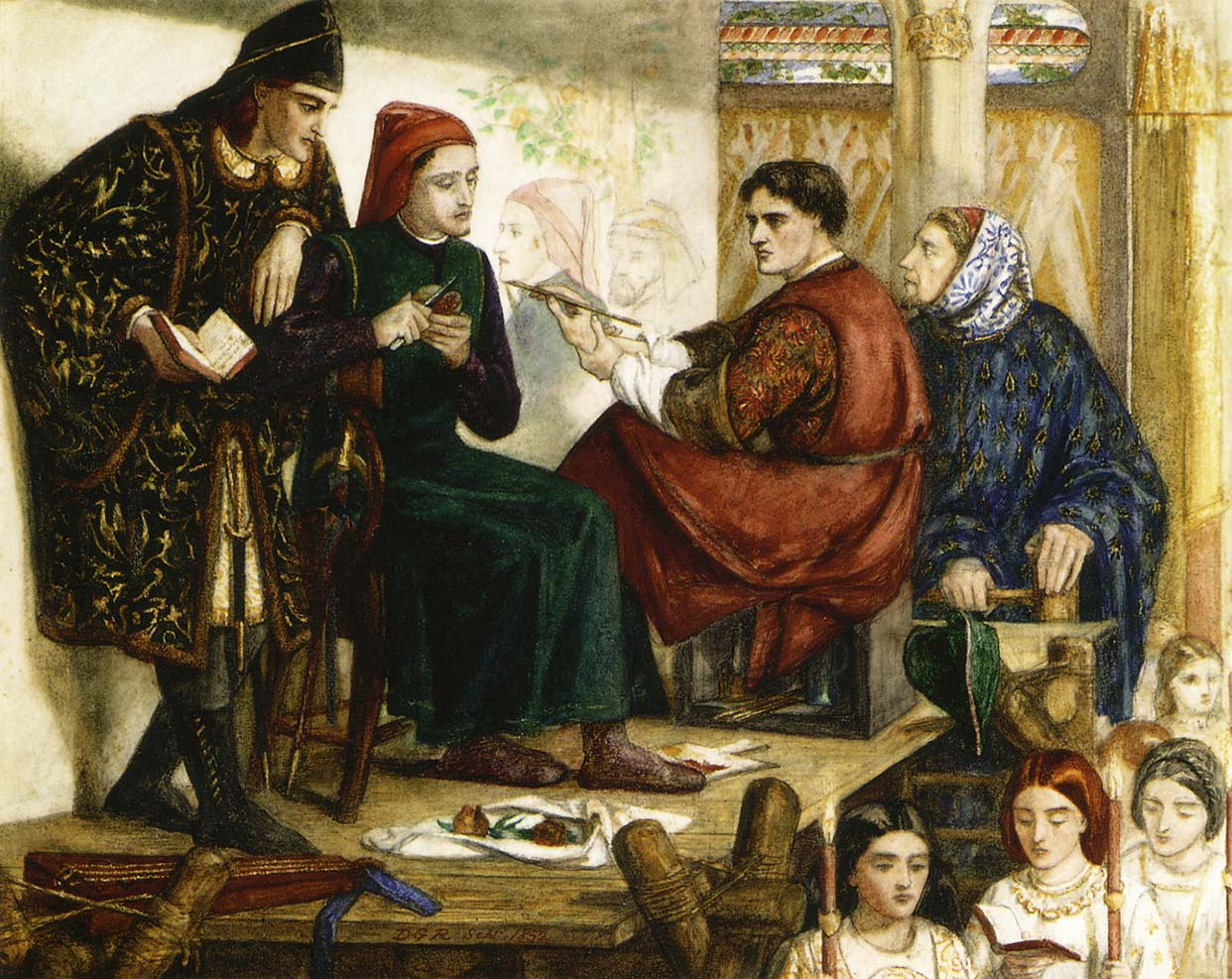
Recently, I was privileged to speak with Dr Francesco Ricatti, Associate Professor of Italian Studies at the Australian National University who kindly arranged the interview which was intended for his second year Italian language students. Our conversation was about Matteo Bandello’s Romeo and Juliet: the Italian novella that inspired the Shakespeare play we all know. I have embedded the video of the interview below. Also, as time didn’t allow, below are a few further thoughts to further explore Bandello, his life and his writing and particularly his Romeo and Juliet. Matteo Bandello: A Refugee Whose Writings Reached the World Starting with Matteo Bandello’s life, in the video we discuss how…
-
Giustina Rocca of Trani: The World’s First Woman Lawyer?
As we near the end of the nineteenth century, in country after country, we see women breaking through gender barriers. This was true in the law as much as in other fields. Giustina Rocca lived in the fifteenth century. Some say she is Italy’s, or indeed, the world’s, first woman lawyer. She was a native of the beautiful coastal city of Trani in Puglia. The city and local legal profession still celebrate her story. They are not the only ones to honour her. The European Court of Justice has named one of its three buildings the Rocca tower in her memory. However the real story is always more involved than…
-
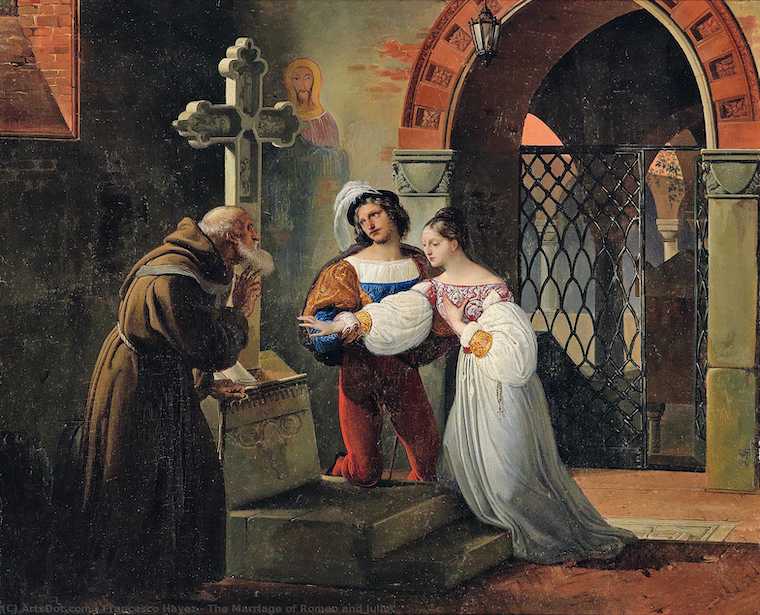
Matteo Bandello’s Forgotten Tale of the Tragic Lovers Romeo and Juliet
Sometimes, you just can’t believe what you turn up in history. If I told you a rather odd (and almost forgotten) bishop was the one who started the story of Romeo and Juliet ‘going global’, you would raise your eyebrows. But that’s what happened. His name was Matteo Bandello, and he wrote Romeo and Juliet before Shakespeare. In fact, he wrote hundreds of stories. And translated into French, English and Spanish, his stories made their way around Europe in his own lifetime. In England and Spain, his stories were adapted for the stage. Shakespeare loved Matteo Bandello’s stories so much, that he made four of them into plays. How did…
-
It’s funny, but Shakespeare is teaching me Italian stories
It’s curious to find the heart of Italy in the soul of England, but so it is. For Shakespeare put it there. For years now, I’ve been hunting down Italian stories, and the last thing I expected was that Shakespeare would give me the breakthrough I was looking for. The most desperate loves, the vilest deceptions, the most delightful cross-dressing dalliances and the bitterest revenge. Shakespeare found them in Italian novellas and adapted them to the London stage. I have to admit, although the journey has been fun, it’s not so easy to plunge into the ocean of Italian literature, not knowing where it might take you or in which…
-
Shakespeare in Love: A Case of Cultural Appropriation?
Shakespeare didn’t write Romeo and Juliet. No! Wait, what? Shakespeare didn’t write Romeo and Juliet!?? That’s right. If the fact Shakespeare set the play in fair Verona didn’t give it away, Shakespeare didn’t create the story of Romeo and Juliet. So no, Shakespeare’s first draft of Romeo and Juliet didn’t read “Romeo and Ethel, the Pirate’s Daughter” as Shakespeare in Love portrays it. And, plot spoiler, no true-life English love of Shakespeare’s inspired the character Juliet. Nor was the war of the two houses of Verona “both alike in dignity” inspired by two playhouses duking it out for writers and audiences in London. Don’t get me wrong. I loved the…
-
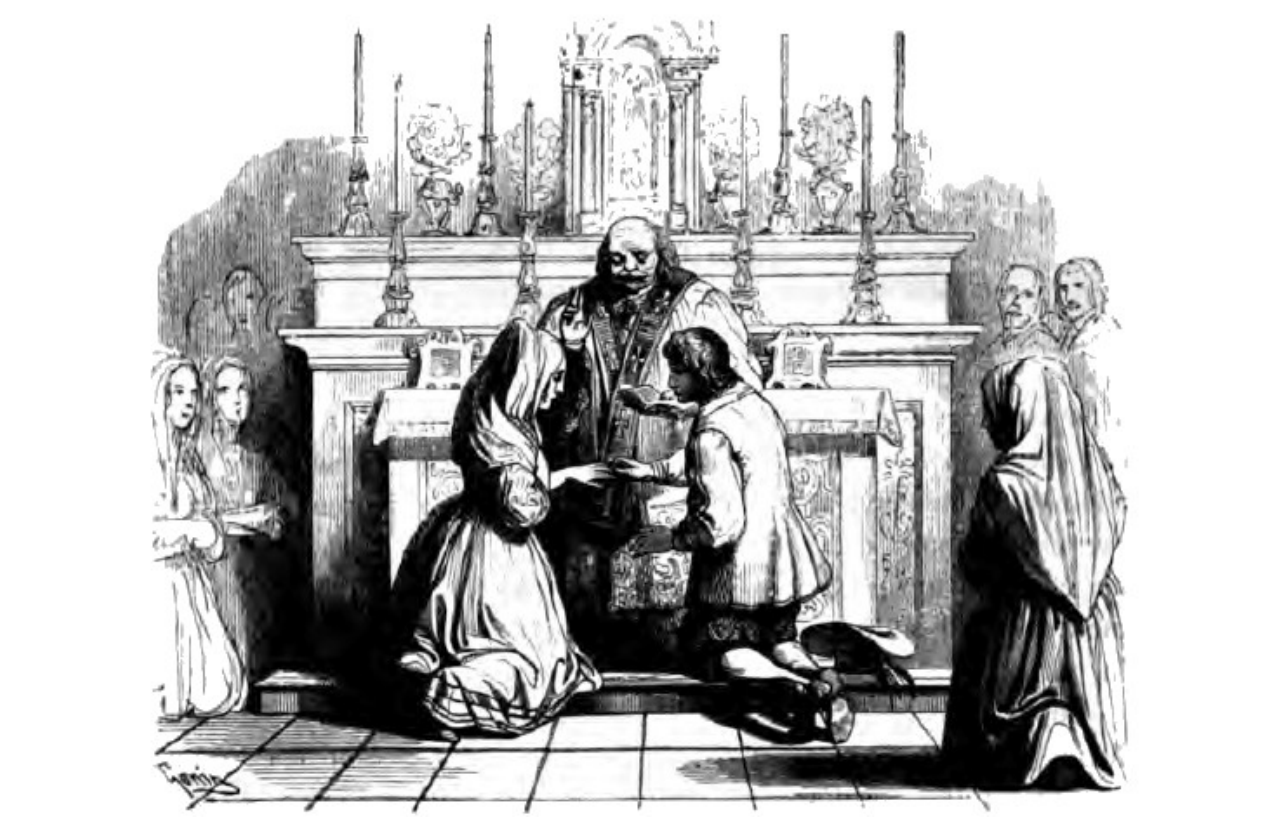
Alessandro Manzoni and the Betrothed (I Promessi Sposi)
Alessandro Manzoni is a talented story teller and a perceptive observer of character. His novel, the Betrothed (I Promessi Sposi) has been celebrated as a gem of Italian literature ever since its publication. It is readily available as a physical, ebook or audiobook (see below) and several movie and serial versions have been made. The novel’s main characters, Renzo and Lucia are in love and they are to be married. Yet achieving this happy and unexceptional outcome turns out to be far from easy in Lombardy of the 1600s in which the historical novel is set. Manzoni wrote his book in the early 1800s, two hundred years later, so we see a more…