refugees
The way in which refugees are excluded is one of the most serious human rights issues facing non-citizens. Refugees may find themselves denied a wide range of human rights including such basic rights as freedom, the right to work, the right to education and the right to safety. Thousands of asylum seekers have lost their lives seeking to cross international borders.
-
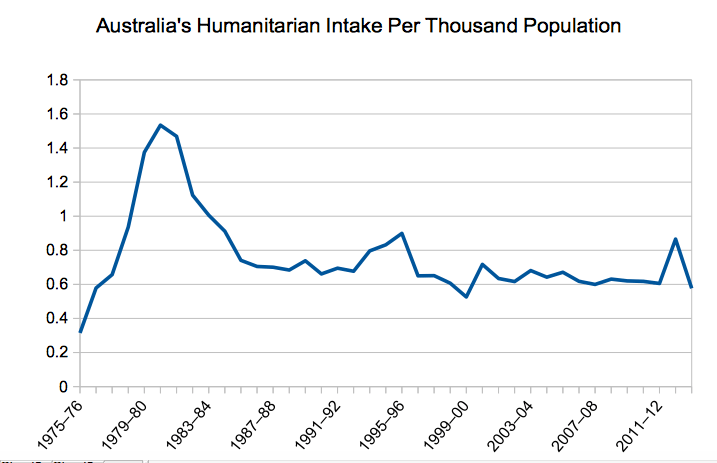
Australia’s refugee intake at historic lows
Update November 2016: Since this post back in 2015, Australia has announced a special humanitarian intake for Syrian refugees. According to information published by the Department of Border Protection, in the 2015-16 year, 17,555 humanitarian visas were issued including almost 3800 to Syrian refugees. In a discussion paper issued for the 2015-16 year, the Department estimates that the 2019 program will be no less than 18,750 places. Meanwhile the global situation for refugees is no better. Such improvements while welcome are insufficient to the need. Australia cannot solve the problem alone. Yet, it is important to continue to ask if we are doing all we reasonably can and should in…
-
A refugee journey out of endless war
The anonymous words below come from the reflections of a young person who arrived in Australia as a refugee. She was when she wrote in Australian immigration detention. Her words were submitted to the national inquiry currently being undertaken by Australian Human Rights Commission into children in immigration detention. Links to national inquiry and her full submissions are provided below. Her story tells a refugee journey out of endless war. I am a young Somali girl who face hardest moment in life. I am 18 years old. I was born in Somalia where horror was basic need in our everyday life. I am a simple person who hides a thousands…
-
Fifty Million Refugees and Displaced People
Not since World War II have there been more than fifty million refugees and displaced people in the world. On 19 June 2014 the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees announced that this total had been exceeded in 2013. Half of those displaced are children.The primary cause of this increase in human suffering are violent conflict in places such as Syria, South Sudan and the Central African Republic. With fifty million refugees and displaced people in the world it is fair to call it a global crisis. yet the global response has been business as usual. Some countries have actually reduced their refugee quotas despite the global crisis.
-
A Fitting Memorial
On or around 14 November 2010 another 97 men, women and children lost their lives as asylum seekers crossing the sea to Australia. The recent Four Corners report (which focussed also on the people smuggler network involved) explored something of the lives of those lost. We here record their names, and what few details that Four Corners published concerning their lives. Such a listing can never be a fitting memorial. Among them was 24 year old Mohammad Rezaie whose fiance waited for him in Melbourne. He left home the day after his sister’s wedding. Ayad Al Kazami his wife and Hiba and Huba, their two daughters, were also on the boat. They also…
-
The borders of virtue and power
Closing borders: to refugees, to undocumented migrants, raises questions of virtue and questions of power. The public debate around borders is so fractured, so superficial, so bedevilled with assumption and ritual conflict that it conveys little new meaning. It simply reiterates the existence of a continuing contest – a contest that often is more about power than rights. In this contest we see progressively increasing brutality and violence. Resort to force, implicit or explicit, is the modern day tool of choice underpinning this public debate. Whether in the sophisticated armory and defenses of international borders or the increasing instances of riot of those who assert their freedom. The tiny island of Lampedusa saw such an example this…
-
Three reasons for Abandoning Mandatory Detention
A paper delivered at a roundtable on alternatives to detention held in Canberra, June 9 – 10, 2011 By Penelope Mathew Freilich Foundation Professor The Australian National University Why does mandatory detention of asylum seekers continue in Australia when there are alternatives? In this short presentation, I invite people to think about three important issues that shape the debate about Australia’s policy of mandatory detention – legality, proportionality and risk. I begin with legality, because it is clear that one of the obstacles to alternatives to detention is the perception that unauthorized arrivals seeking asylum have acted illegally. One reason for this perception is that human rights law speaks with…
-
Do Foreigners Have the Same Human Rights as the Rest of Us?
At the core of human rights is the axiomatic truth that human beings have inherent rights: that all human beings are equal and possessed of dignity and that violation of such rights is both morally offensive and legally impermissible. An alternative ordering of human relationships is mandated by exclusive national citizenship. Implicitly and explicitly national citizenship counsels the primacy of the privileged ‘citizen’ over the ‘non-citizen’ ‘other’. Everywhere we see the manifestation of this ordering in gross, systematic and widespread human rights violations: in our laws, practices, attitudes and media. Some of ‘us’ are the privileged beneficiaries of those violations: and we violate the human rights of foreigners as if…
-
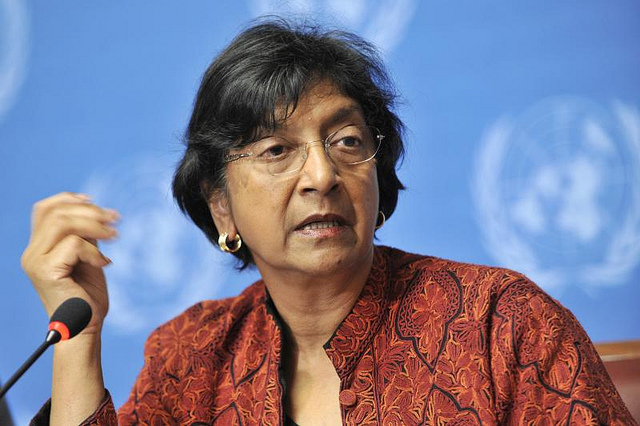
UN High Commissioner for Human Rights in Australia
As, UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Navi Pillay, today acknowledged there are a lot of human rights positives for Australia, but there were two issues on which Australia’s record is troubled: Australia’s treatment of indigenous Australians and asylum seekers. “In my discussions with Aboriginal people, I could sense the deep hurt and pain that they have suffered because of government policies that are imposed on them. I also saw Aboriginal people making great efforts to improve their communities, but noted that their efforts are often stifled by inappropriate and inflexible policies that fail to empower the most effective, local solutions. I would urge a fundamental rethink of the measures being…
-
Why Global Citizenship?
1. Introduction Plutarch said: … nature has given us no country as it has given us no house or field. … Socrates expressed it … when he said, he was not an Athenian or a Greek, but a citizen of the world (just as a man calls himself a citizen of Rhodes or Corinth).[1] Plutarch urged his audience to become conscious of a wider reality and to exercise their imagination to overcome a narrow, localised conception of their identity. That is the role of my global citizenship claim too. Plutarch and Socrates did not conceive of the world as a globe,[2] as I do: I have travelled across the world;…