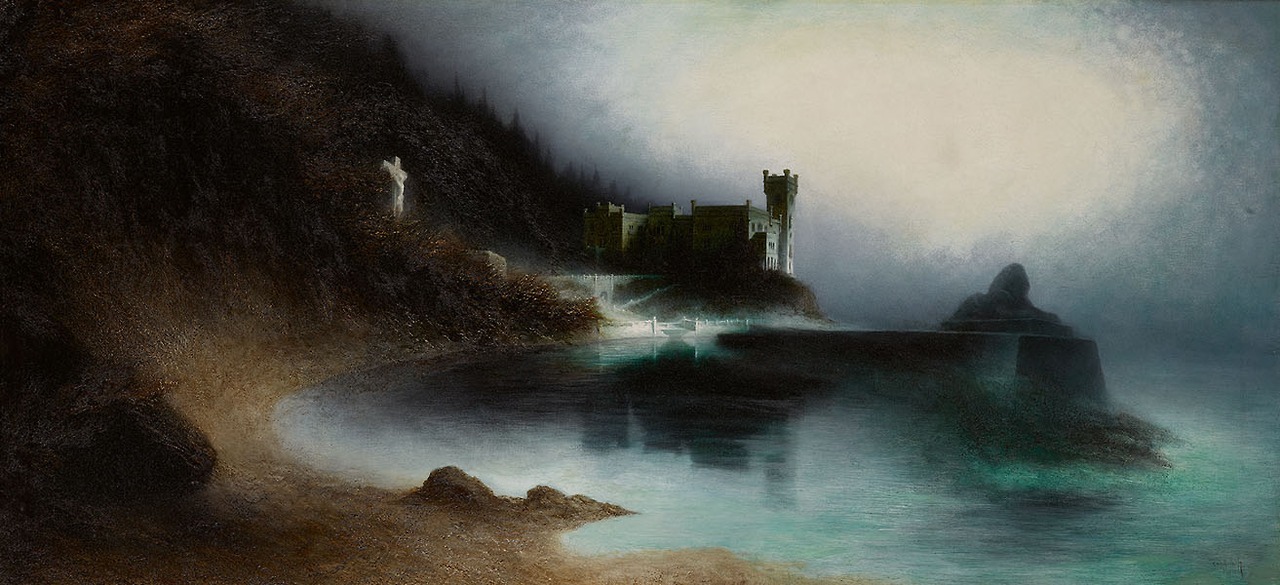-
When Malaria in Italy was a National Disease
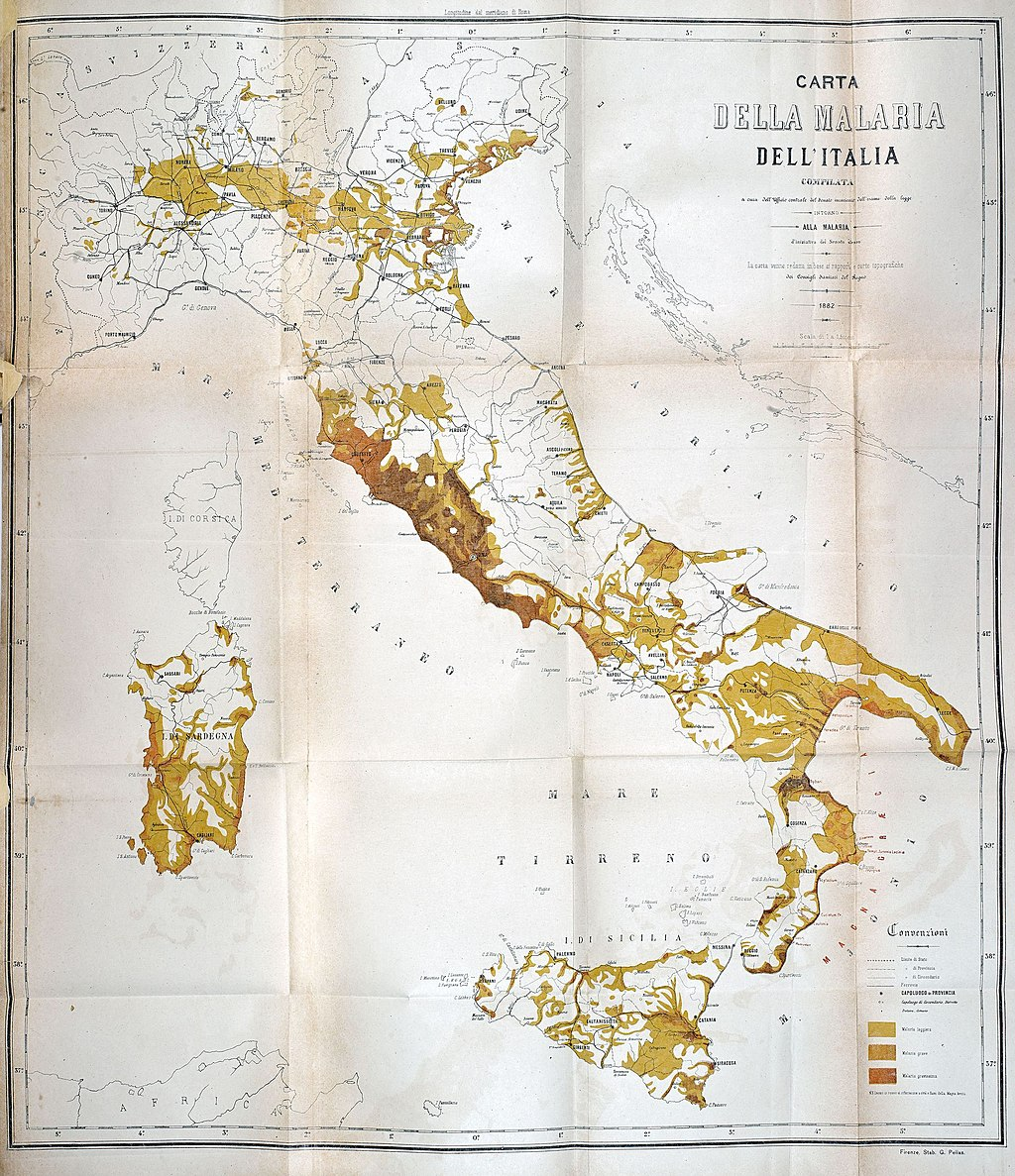
At the end of the 19th century, up to 20,000 Italians died every year from malaria and millions were infected. Even the word is Italian: “la mal’aria” – the bad air – a phrase to describe the mysterious and then unknown causes of the disease, which was attributed to the “bad air” of swampy ground. Malaria arrived in Italy in ages past, and was there when the ancient Greeks began to build their cities on Italy’s shores. The story of the effects of malaria is recorded in the collapse of the once flourishing city of Posaedonia (today Paestum). Founded about 600BC, its ancient Greek temples still draw tourists from around…
-
Caruso: Dalla’s Song of Love, Pain and Death
The song Caruso has genius in its verses, and it is one of the most popular songs Italy has given the world. The verses of Caruso came to singer songwriter Lucio Dalla in a burst of inspiration. “Ti voglio bene assai”: I love you very much. Such words (in any language) are among the most meaningful human beings share with each other.They are words which, with “Tanto tanto bene sai” – So much, so much, you know, resonate in the chorus of the song. Yet these words are not where the song begins. Rather we are on a Terrazza, overlooking the “Golfo di Sorriento“. It is one of Italy’s most…
-
Giosuè Carducci and Miramar Castle
Mexico gifted Italy the tomato. Italy sent back an Emperor. It wasn’t a fair exchange. And it wasn’t welcomed. The story begins in Miramar Castle and Giosuè Carducci is our story teller and his poem Miramar can be read below. Carducci came to the castle when it was already a place where ghosts whisper of the past. However the journey that took him to the castle passes through one of the most turbulent eras of Italy’s history. Carducci was born in 1835 and lived to see the birth of the new country of Italy. However he was not just a passive spectator. He was a passionate advocate of the Risorgimento.…
-
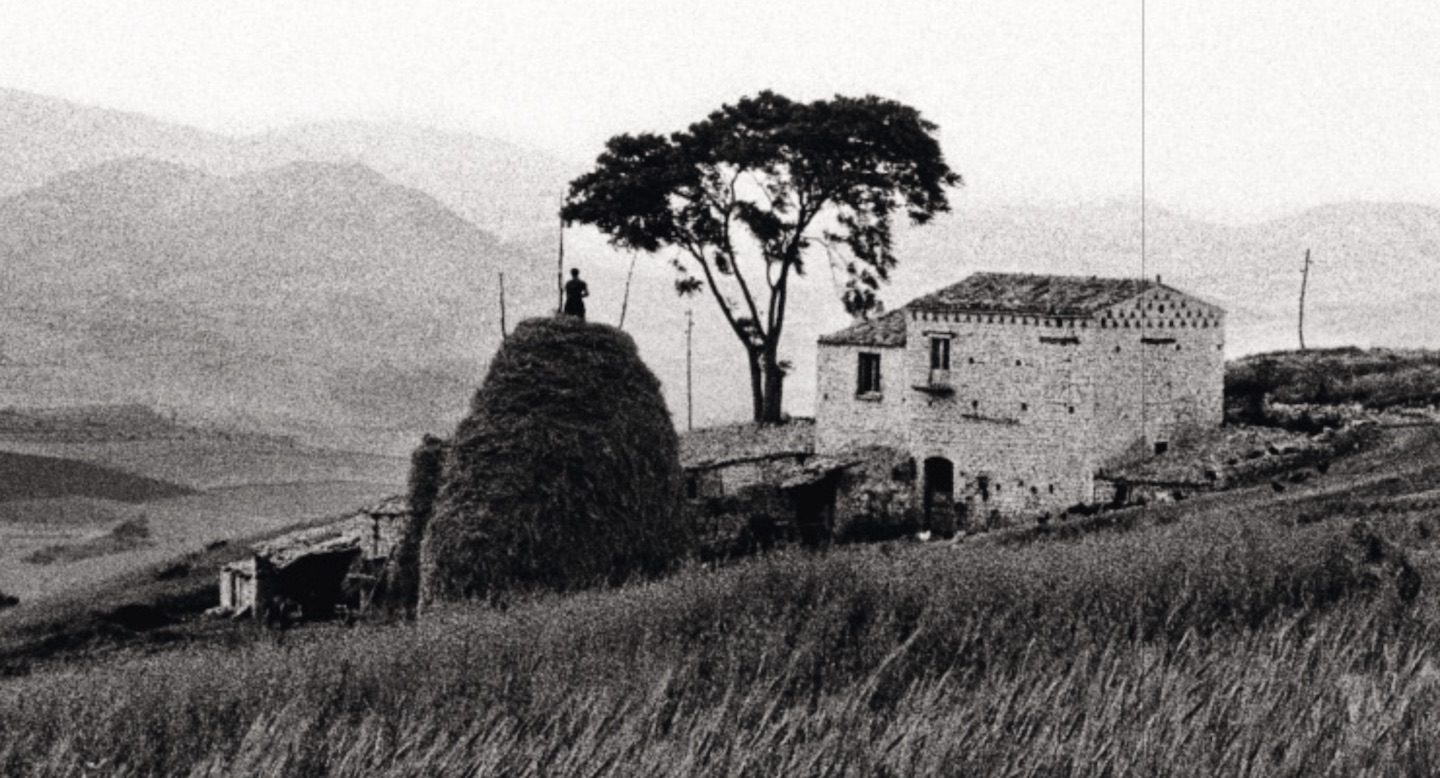
Lacedonia – Frank Cancian’s Pictures of a Disappearing World
In 1957, it must have been a trip of a lifetime. Frank Cancian was going to Italy. An American student, child of Italian immigrants, he had won a Fullbright scholarship. The project would combine his love of photography and his studies in anthropology. He would use his camera to document the life of Lacedonia, a town in the hills of Avellino. To reach Lacedonia you have to climb into the Apennines to the east of Naples. In ancient times this had been the land of the Samnites, Rome’s bitter enemies, who had long resisted conquest. Later it became the border lands of southern Lombard duchies before the Normans placed their…
-
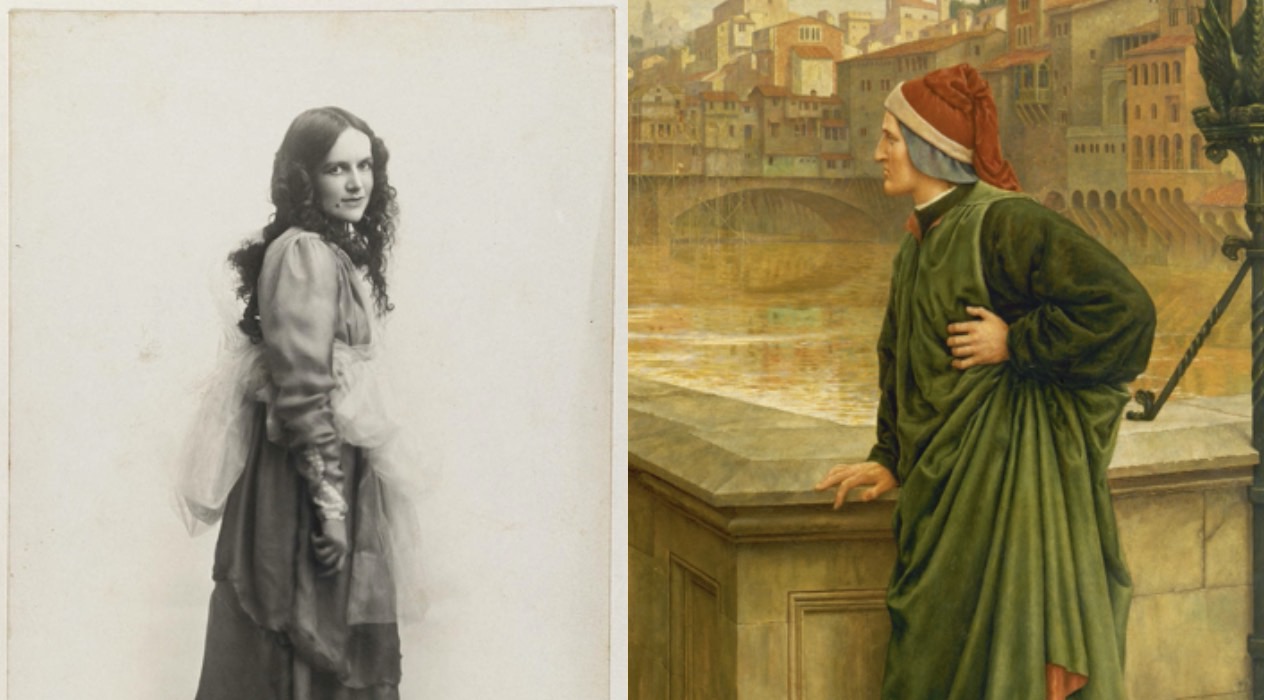
Dante Alighieri in a Wide Brown Land*
On the hill beyond Canberra’s lake we do not find ourselves in Dante’s dark wood. Instead, the hundred carefully nurtured forests of the National Arboretum surround us. Some of its trees are from Australia, but many are from far beyond. As we appreciate their beauty, we see that these forests can symbolise Italians in Australia,[1] for we are part of the diverse heritage of this continent. Yet as our eyes turn to the ridge near the Himalayan Pines, we see a rusted monument rise from the land before us.[2] It is timeless, as it proclaims Dorothea Mackellar’s words “Wide Brown Land”. She wrote them about Australia in 1907; a young…
-
Prendiamo un caffè? Italian Coffee Culture
Let’s face it without the caffè this morning (yes, made with a traditional Italian caffettiera), I wouldn’t be writing this. Names like espresso, cappuccino, latte, and the now ubiquitous Italian espresso machines are a standard part of Australian cafe culture. So it’s natural to assume there is something quintessentially Italian about coffee. As Simona Lidia, a blogger on Italian culture jokes “an Italian will always believe deep inside that coffee grows spontaneously in Italy, and only in Italy, since the Lower Paleolithic.” Living Italian Coffee If my experience is anything to go by Italians, even in diaspora, can’t escape Italian coffee culture. Growing up, the tiny white cups were there…
-
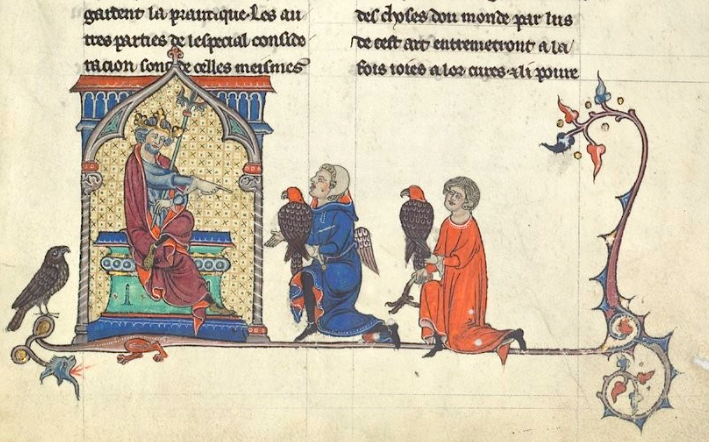
Emperor Frederick II, the Wonder of the World and the Art of Falconry
Frederick II has been praised to the heavens and condemned to the depths of hell (by both Pope and Poet). The Son of Apulia, Wonder of the World, Holy Roman Emperor, perjurer and sacrilegious heretic, “Sultan” of Lucera, violator of his pledge as crusader, peaceful liberator of Jerusalem, enlightened patron of science and founder of universities, brutal in the extreme, law maker, the lamented sunset of the glory of Norman Italy. He has been called the first European and the “first modern man to sit on a throne”. He was also the author of “The Art of Falconry” or de Arte Venandi cum Avibus. Such are some of the memories…
-
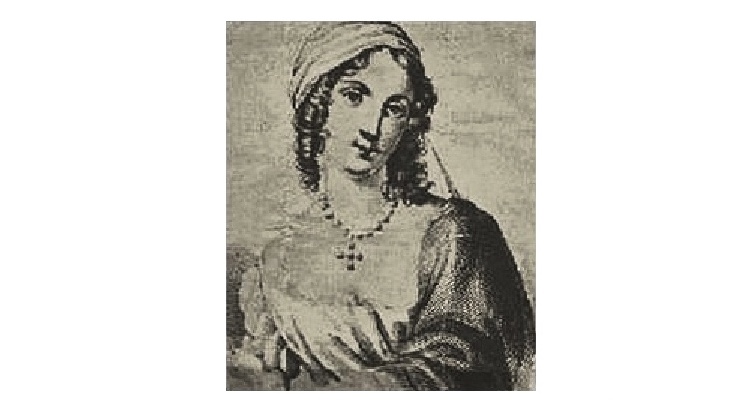
Matilde Serao and the Life of Cristina
Matilde Serao was unusual. In 19th century Naples, she was a successful journalist, writer and newspaper proprietor. Her fiction was widely published and quite a few of her works were translated into English in her own lifetime. Cristina is the main character of Matilde Serao’s short story of the same name. But Cristina lives in another world. The story’s opening words begin to sketch its nature. While Cristina leant over to gather a fragrant clump of basil with which to flavour her tomato sauce boiling in the kitchen, she heard a brief and sweet whistle. Mentre Cristina si chinava a cogliere un ramoscello di basilico odoroso, da mettere come aroma…
-
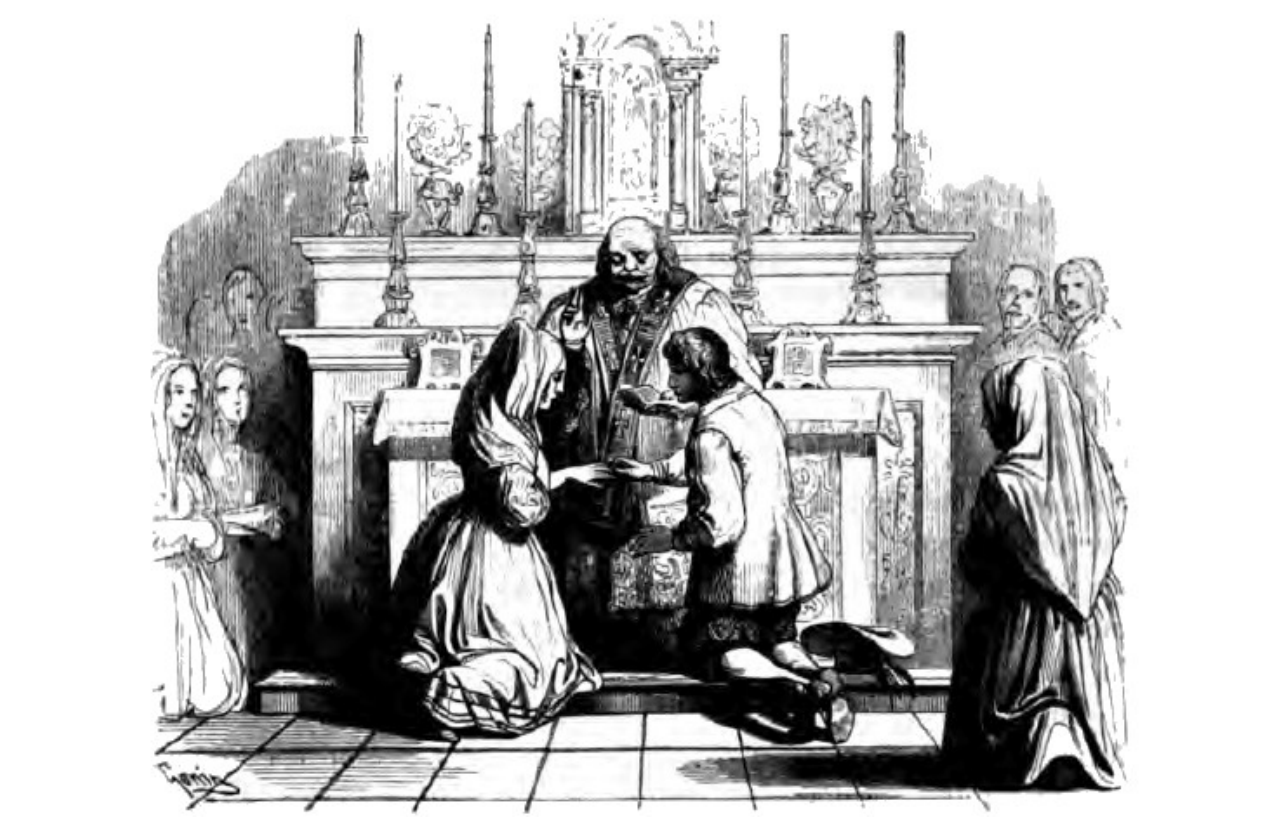
Alessandro Manzoni and the Betrothed (I Promessi Sposi)
Alessandro Manzoni is a talented story teller and a perceptive observer of character. His novel, the Betrothed (I Promessi Sposi) has been celebrated as a gem of Italian literature ever since its publication. It is readily available as a physical, ebook or audiobook (see below) and several movie and serial versions have been made. The novel’s main characters, Renzo and Lucia are in love and they are to be married. Yet achieving this happy and unexceptional outcome turns out to be far from easy in Lombardy of the 1600s in which the historical novel is set. Manzoni wrote his book in the early 1800s, two hundred years later, so we see a more…