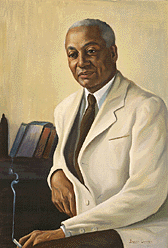-
We are One – Overcoming Racism: Part 2
As introduced in yesterday’s article, racism is entirely incompatible with Bahá’u’lláh’s teachings. Close your eyes to racial differences, and welcome all with the light of oneness.[1] As Westerners began to join the Baha’i Faith early in the 1900s, it was clear that racism would need to be addressed, and ‘Abdu’l-Bahá, Bahá’u’lláh’s eldest son, set out to do so. Indeed ‘Abdu’l-Bahá began this work from the earliest visits of Western pilgrims who came to see him in the early 1900s to learn about Bahá’u’lláh’s teachings. In 1911 he invited Louis Gregory, an African American lawyer, to visit him. The pilgrimage not only had a profoundly transformative spiritual impact on Gregory but provided opportunities for ‘Abdu’l-Bahá to stress…
-
The Poetry of Langston Hughes
Racism and problems of race relations continue to generate injustice and racial animosity around the world. The problem is not confined to any one people or country, but the case of the United States is better known in the English speaking world. The poetry of Langston Hughes comes from a period in which racism had reached a peak – what is known as the “Jim Crow” era. The United States civil war ended slavery, but it didn’t end racism. Gradually racism took a stronger hold in society and by the early 20th century it gave rise to toxic theories of racial supremacy and scientific racism. A fierce segregation was instituted between…
-
Alain Locke on Identity and Human Rights
Of Alain Locke, Martin Luther King Jr. said: “We’re going to let our children know that the only philosophers that lived were not Plato and Aristotle, but W. E. B. Du Bois and Alain Locke came through the universe.” In this article we explore an idea in the work of Alain Locke – the idea that identity and oppression are related to each other. That the pathway to emancipation is through re-imagining our identity. Early on he explored these themes in the introduction he wrote to his 1925 anthology titled “The New Negro“. The tribute above, particularly from Martin Luther King, calls for greater attention to Alain Locke’s philosophy and…
-
Martin Luther King Jr – Civil Rights Leader and Peace Advocate
Martin Luther King, Jr. gave his life for the poor of the world, the garbage workers of Memphis and the peasants of Vietnam. The day that Negro people and others in bondage are truly free, on the day want is abolished, on the day wars are no more, on that day I know my husband will rest in a long-deserved peace. —Coretta King This article is part of a series on human rights forebears. Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. lived a life beyond the ordinary and writing about him is challenging. His life made the world that came after him better. This article will not do justice to his…
-
The Peace Advocacy of Martin Luther King (Part 4 of 4)
To appreciate Martin Luther King’s thoughts on peace, we must understand his thoughts about the relationship between human beings. He saw all human beings as caught “in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny.” He expands on this thought in his 1964 speech, “The American Dream”. All I’m saying is simply this, that all life is interrelated. And we are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny — whatever affects one directly, affects all indirectly. For some strange reason I can never be what I ought to be until you are what you ought to be, and you…
-
Martin Luther King and Non-violence (Part 3 of 4)
Martin Luther King thought deeply about the best methods to use to overcome the injustices facing African Americans. This in itself is an important observation. It is appropriate for us in the 21st century to also think deeply about questions of method. His speeches frequently describe and defend nonviolence as the method he felt was both effective and moral for the issues on which he worked. Sometimes the description was in response to criticism of the method as “too extreme”, at other times it was to reject the violence advocated by some. His explanations were patient and detailed. The basic steps of the method are outlined to his fellow ministers…
-
Martin Luther King Jr. – What role did Christianity play in his civil rights advocacy? (Part 2 of 4)
Martin Luther King Jr. was born in Atlanta Georgia, the second son of Martin Luther King Sr. and Alberta Williams King. Martin Luther King Jr. was by vocation a Baptist minister. He was in the fourth generation of his family to take up this vocation. It is impossible to fully appreciate Martin Luther King’s work without understanding the role that Christian thought and inspiration played in his advocacy of human rights. Martin Luther King’s letter from a Birmingham prison to fellow Christian clergymen gives insight to the role his religious commitment played in generating and sustaining his commitment to work for justice. Further, the people from whom he came, the…
-
Martin Luther King Civil Rights Leader and Peace Advocate (Part 1 of 4)
Martin Luther King, Jr. gave his life for the poor of the world, the garbage workers of Memphis and the peasants of Vietnam. The day that Negro people and others in bondage are truly free, on the day want is abolished, on the day wars are no more, on that day I know my husband will rest in a long-deserved peace.—Coretta King This article is part of a series on human rights forebears. Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr lived a life beyond the ordinary and writing about him is challenging. His life made the world that came after him better. This article will not do justice to his contribution.…