-
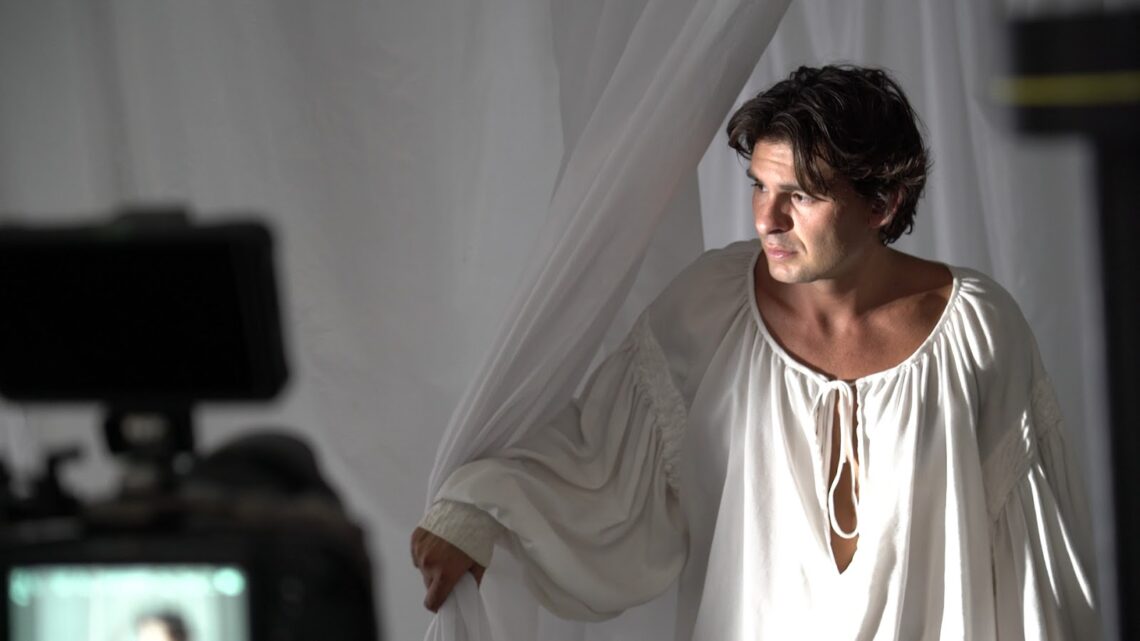
Behind the scenes interview: Juliet is dead: Romeo’s Lost Scene
In the video below, director filmmaker Rhianna Spooner and author/translator Michael Curtotti talk about Juliet is Dead: Romeo’s Lost Scene: the new release short film dramatising a lost scene from the Romeo and Juliet story. That scene never made it into Shakespeare’s play. The video includes behind the scenes footage from the film shoot with J.K Kazzi and Gabriel Alvarado. An edited interview transcript (not including the behind the scenes footage in the video) is provided below. Introduction Hi, my name’s David Curry. I’m coming to you from Ngunnawal and Ngamberri country, Canberra. I’m very excited to be part of this launch of Juliet is Dead: Romeo’s Lost Scene. So…
-
Romeo and Juliet Go Down to Egypt
As far as we know, the first recognisable version of Romeo and Juliet was written by Masuccio Salernitano, or, by his proper name: Tommaso Guardati. (His nickname just means: “Tommy of Salerno.”) In 1476, when he wrote his version of Romeo and Juliet, he didn’t use the names we now know today. Yet even though he calls the lovers “Mariotto and Gianozza,” and they lived in Siena instead of Verona, it’s clear these lovers are Romeo and Juliet. The journey from Masuccio’s tale to that of Shakespeare passes through several versions. First, Luigi da Porto took the story and put it in Verona. He gave the lovers the names we…
-
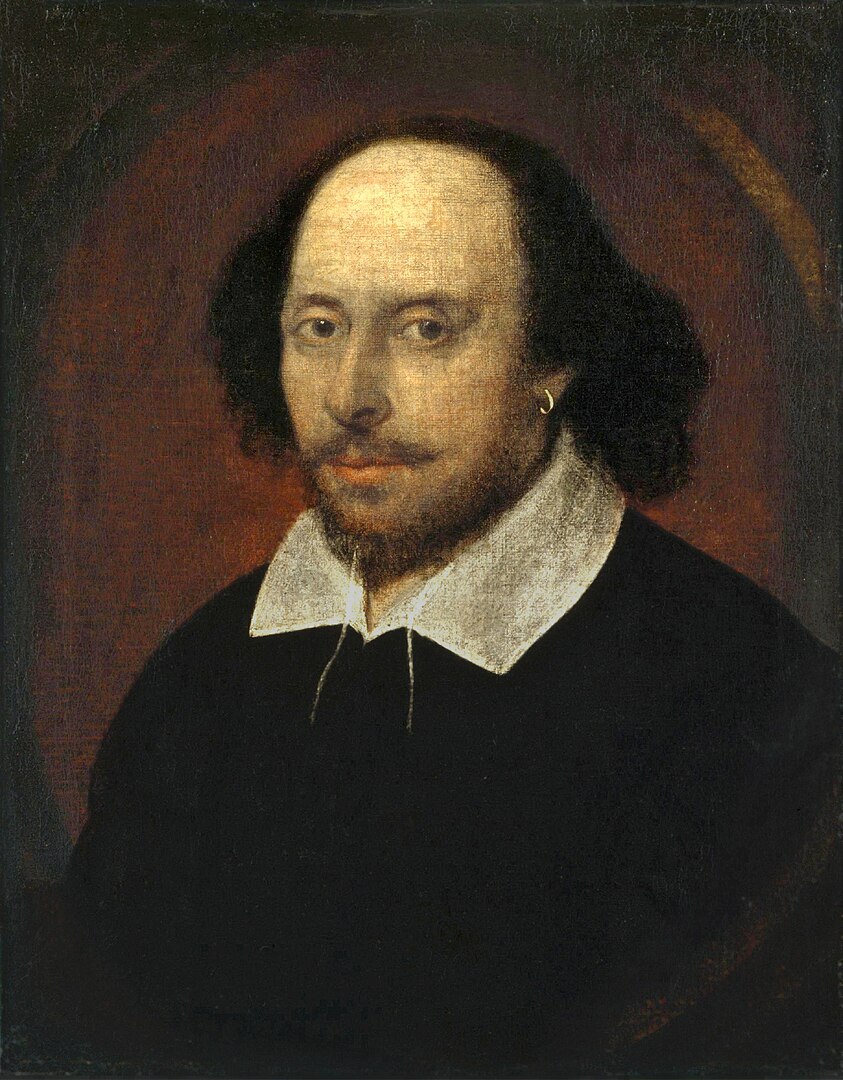
What an Italian novella really taught me about Shakespeare …
It’s a strange place to look, you’d think. Shakespeare is an English poet. No … He is the English poet. So surely there would be little to learn about him in an Italian story, particularly one written before he was even born. But that’s the great thing about taking a turn down the side roads of history. You never know what you’ll discover. Earlier I wrote an article titled: It’s Funny, but Shakespeare is Teaching me Italian Stories. This is a complement and looks at the relationship between Italy and Shakespeare from the opposite direction. But where to begin? That maybe there was a grain of truth in a Groats-worth…
-
Matteo Bandello’s Forgotten Tale of the Tragic Lovers Romeo and Juliet
Sometimes, you just can’t believe what you turn up in history. If I told you a rather odd (and almost forgotten) bishop was the one who started the story of Romeo and Juliet ‘going global’, you would raise your eyebrows. But that’s what happened. His name was Matteo Bandello, and he wrote Romeo and Juliet before Shakespeare. In fact, he wrote hundreds of stories. And translated into French, English and Spanish, his stories made their way around Europe in his own lifetime. In England and Spain, his stories were adapted for the stage. Shakespeare loved Matteo Bandello’s stories so much, that he made four of them into plays. How did…